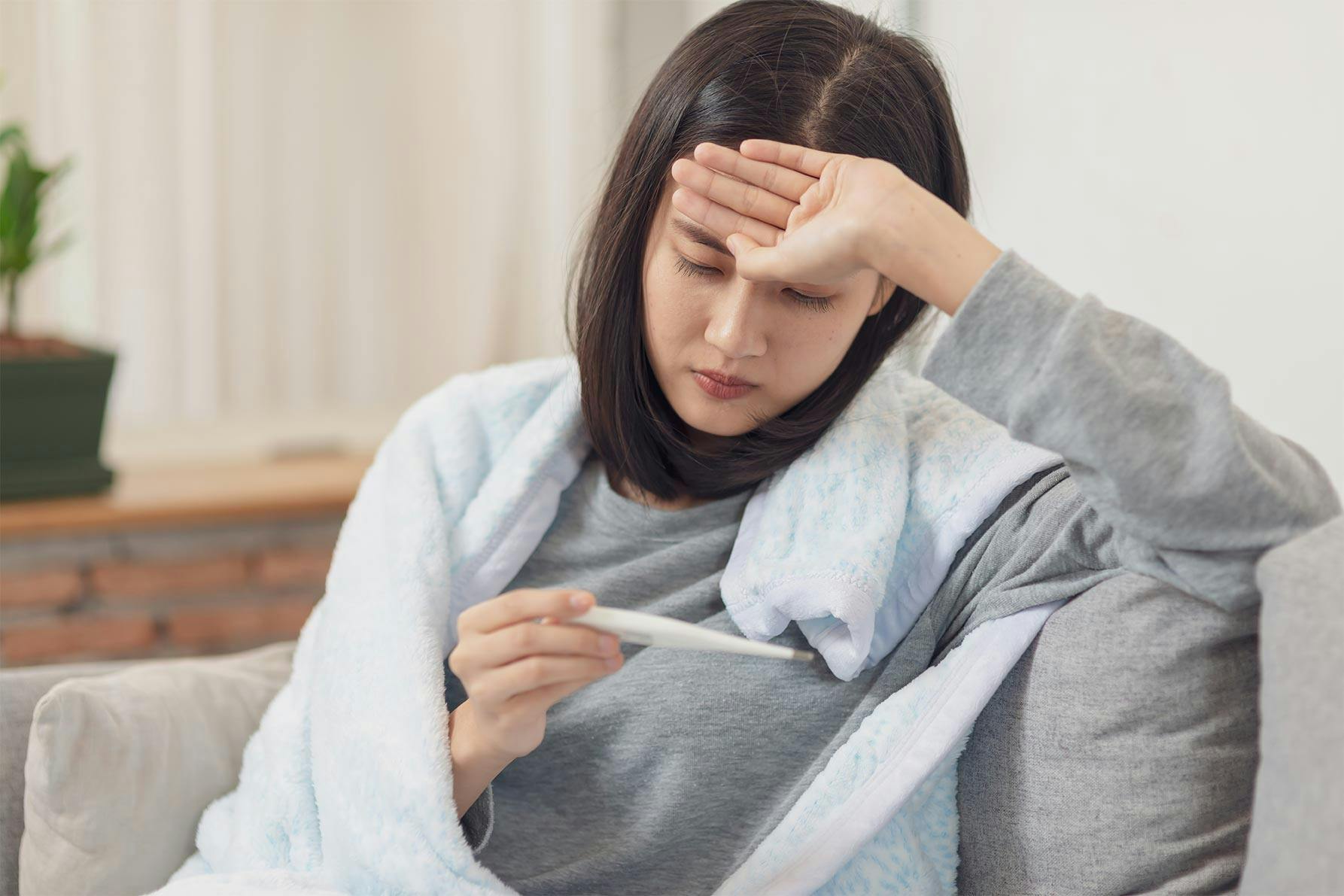
Even though it doesn’t always feel great, believe it or not, a fever in an adult can be a good sign. 1,2,3,4,5 As the body’s natural response to infection, a fever can signal a healthy immune system doing precisely what it’s meant to do. 1,2,3,4 Learn more about what causes a fever, related symptoms, taking ibuprofen for a fever and when to seek medical care.
Key Takeaways
- A fever in adults is often a natural immune response to infection and is considered low-grade at 99.6–100.3°F, standard at 100.4–102.9°F, and high-grade at 103°F or higher.2,4 Knowing these ranges helps determine when to monitor versus seek medical care.
- Ibuprofen, the active ingredient in Advil, effectively reduces fever and pain caused by inflammation, offering fast relief by blocking the chemicals that cause pain and heat, especially when fever symptoms like muscle aches or headaches appear.6
- Although fevers often resolve on their own, supportive care such as rest, hydration, and light meals—along with over-the-counter options like Advil—can provide comfort and help manage symptoms while the body recovers.1,2,3,4
What Constitutes a Fever?
When your body temperature temporarily rises above normal levels, you have a fever.1,2,3 The normal average temperature is 98.6°F. Given natural fluctuations based on time of day, activity and environment, the normal range is 97-99.5°F.4 In adults, a standard-grade fever is when your internal temperature reaches 100.4°F.2,4 These are the fever grades in adults based on body temperature:2,4
- Low Grade: 99.6-100.3°F
- Standard: 100.4-102.9°F
- High Grade: 103°F or higher
What’s the Best Way to Take an Adult’s Temperature?
While forehead, ear and strip thermometers are particularly convenient, they aren’t the most accurate option for gauging body temperature.1 Rectal thermometers provide the most accurate reading for children.4 For older children and adults, the most accurate results are found under the armpit or in the mouth.4
What Causes a Fever in Adults?
Viral infections are the most common cause of fever in adults. 2 Those include the common cold, flu and COVID-19. 3 Bacterial infections, such as urinary tract infections and pneumonia, can also cause fever. 3,4 In fact, many illnesses and activities can raise body temperature, including a reaction to an allergen and becoming overheated in the sun. 4
What Are the Common Symptoms of a Fever?
In addition to throwing off your internal temperature, fevers can occur along with other effects in the body. 1 Here are some common symptoms adults may experience when they have a fever:1,4
- Weakness
- Irritability
- Sweating
- Severe headache
- Flushed face
- Nausea or vomiting
- Low or absent appetite
- Dehydration
- Shivering and chills
- Muscle aches
These symptoms are considered normal, so they aren’t necessarily cause for medical attention. 1
When Should I Seek Medical Attention?
If you have a high-grade fever, meaning your temperature hits 103°F or higher, it’s time to call your healthcare provider. 1 Seek immediate medical attention if you have a temperature above 103°F alongside any of these symptoms:1,4
- Rash
- Confusion
- Altered speech
- Unusual behavior
- Sensitivity to bright light
- Pain when bending forward along with a stiff neck
- Chest pain or problems breathing
- Pain during urination
- Vomiting and dehydration
- Abdominal pain
- Seizures or convulsions
How Do I Treat a Fever?
While most fevers go away on their own within a few days, there are steps that you can take to reduce your fever and ease any discomfort.1 Here’s what you can do to treat a fever: 1,2,3,4,5
- Rest
- Dress lightly
- Hydrate
- Use a cool compress
- Take a lukewarm bath
- Eat light meals, if hungry
Should I Take Ibuprofen for a Fever?
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and functions by blocking the production of the chemicals that cause inflammation.6 As the term NSAID suggests, these drugs are helpful for the discomfort that accompanies inflammation: redness, pain and heat.6
Ibuprofen vs Acetaminophen for Fever
Ibuprofen is a fever reducer and an active ingredient in Advil products; it treats pain at the source.6 Other OTC painkillers may contain acetaminophen, an analgesic, which blocks the pain signals sent by the brain.6 While research has indicated that ibuprofen and acetaminophen are generally comparable for managing fever in adults, clinical data suggests that Children’s Advil works faster and longer than Children’s Tylenol for managing fever in children.7
While having a fever is no fun, they happen to everyone and often indicate that a healthy immune system is at work. When used as directed, ibuprofen can provide fast and powerful relief. Advil offers over the counter fever and pain relief medications containing ibuprofen for a variety of symptoms and ailments. Quell your pain at night with Advil PM Liqui-Gel Minis and relieve cold and flu symptoms with Advil Multi-Symptom Cold & Flu.
Source Citations:
- Fever. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fever/symptoms-causes/syc-20352759?p=1. Accessed 3/30/23.
- Fever. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10880-fever. Accessed 3/31/23.
- Fevers in adults, children and toddlers: When to worry. Stamford Health. https://www.stamfordhealth.org/healthflash-blog/primary-care/fever-in-adults-when-to-worry/. Accessed 3/31/23.
- Fever. Cedars Sinai. https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/f/fever.html Accessed 3/31/23.
- Fever in Adults. Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/treating-fever-in-adults Accessed 3/31/23.
- Acetaminophen vs. Ibuprofen: What’s the Difference? Cleveland Clinic. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/acetaminophen-vs-ibuprofen-which-works-better. Accessed 4/28/25.
- Efficacy and safety or ibuprofen and acetaminophen in children and adults: a meta-analysis and qualitative review. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK79235/. Accessed 4/28/25