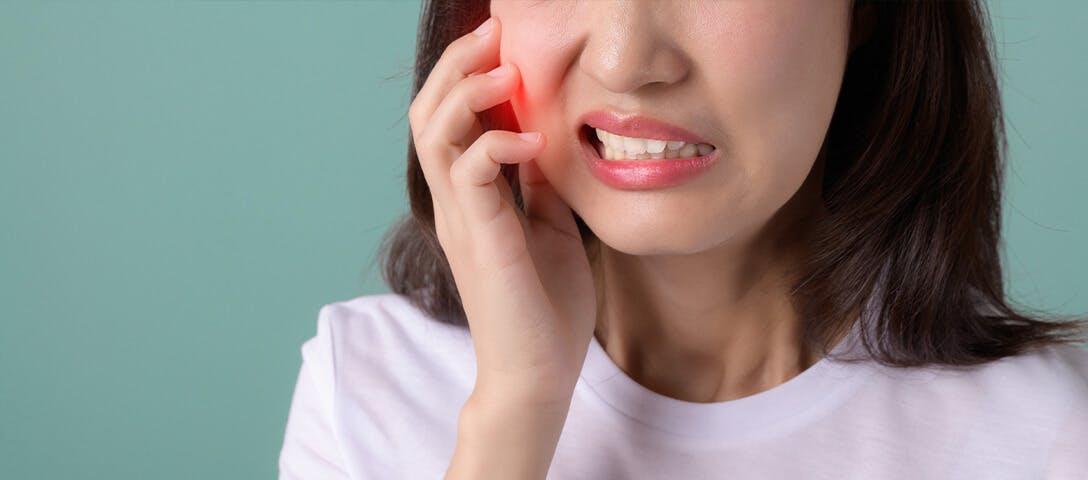
Tooth pain can range from mildly distracting to seriously disruptive. Whether it’s caused by a cavity, gum irritation, or recovery after a dental procedure, finding relief quickly is often a top priority. One of the most recommended options for easing dental discomfort is a class of medicines called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs. These medications, which include ibuprofen (the active ingredient in drugs such as Advil), work by reducing pain caused by inflammation in the gums and surrounding dental tissues.3.4
By blocking enzymes that trigger the production of prostaglandins, which are the substances in the body that cause pain at the site of inflammation,3.4 NSAIDs are effective toothache pain relievers. This makes them useful for short-term pain management until professional dental care is available.
Key Takeaways
- Advil, an NSAID, is an effective toothache medicine that reduces pain caused by inflammation. 3.4
- Gum disease, cavities, and dental procedures often cause swelling, which is the main source of tooth pain.1,2
- Dentists and the ADA recommend NSAIDs like Advil as first-line tooth pain medicine.5
What Causes Tooth Pain?
There are several things that can cause tooth pain, and among the most common are:1
- cavities or tooth decay
- cracked or broken teeth
- infections
- dental procedures
- gum disease
- Dental procedures such as extractions, root canals, or orthodontic adjustments1,2
In many cases, it’s swelling around the teeth and gums that causes the most discomfort. Gum tissues, particularly the papillae (the small triangular sections between the teeth), are prone to inflammation that causes pain. Even small irritations such as food particles lodged under the gum line can trigger swelling and pain.2
How NSAIDs Work to Help Relieve Dental Pain
NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are widely used by healthcare professionals to reduce inflammation, pain and fever.3,4
- Mechanism of action: NSAIDs work by inhibiting COX (COX-1 and COX-2) enzymes from making hormone-like chemicals called prostaglandins, which are one of the body’s biggest contributors to inflammation that causes pain. 3.4
- Applications: Healthcare providers recommend NSAIDs for a wide range of conditions, including dental pain, headaches, arthritis, and muscle stiffness. 3,4
For a deeper dive on NSAIDs, see our on guide on What is an NSAID (and How Does it Work?).
Why Dental Professionals Might Recommend NSAIDs
A new clinical practice guideline from the American Dental Association recommends NSAIDs, with or without acetaminophen, as first-line of defense for managing acute dental pain in adults and adolescents 12 years and older.5
This approach is preferred over opioids due to effectiveness and lower risk of side effects or dependency. NSAIDs are especially useful in situations where immediate dental care isn’t available, or post-procedure pain management is needed.
Practical Uses of Advil as a Medication for Tooth Pain
Knowing when and how to use NSAIDs can help you manage tooth pain safely and effectively. Here are some tips for using NSAIDs:1
- When to take: NSAIDs can be taken in times where dental pain relief is not readily available (e.g., when you have a toothache), or right after procedures like extractions when prescribed by a professional.
- Dosage matters: Always follow your doctor’s guidance or the label instructions. The strength of the medicine, number of doses per day, and duration of use depend on the medical problem being treated.https://www.advil.com/symptoms-tips/pain/how-much-ibuprofen-can-i-take/6
- When to call your doctor: Seek immediate care if pain lasts longer than a couple of days, or if you experience fever, swelling, difficulty swallowing, or other signs of infection.1
Using Advil to Alleviate Tooth Pain
As an NSAID, Advil is a well-studied, effective option for providing relief from tooth pain. By reducing inflammation as a cause of pain, Advil can ease discomfort before treatment and support recovery after dental procedures. 3,4
It’s important to remember, however, that NSAIDs only manage symptoms, and do not address the underlying cause of dental pain. If tooth pain persists or worsens, schedule an appointment with a dentist promptly.
Find the Advil that's right for you to help manage tooth pain until professional care is available.
Source Citations:
- Toothache: First aid. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-toothache/basics/art-20056628. Accessed 9/8/25.
- Gums – swollen. Mount Sinai. https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/gums-swollen. Accessed 9/15/25.
- What are NSAIDs?. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/11086-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-medicines-nsaids. Accessed 9/8/25.
- NSAIDs. Arthritis Foundation. https://www.arthritis.org/drug-guide/nsaids/nsaids. Accessed 9/8/25.
- New ADA guideline recommends NSAIDs to manage dental pain in adults, adolescents. ADA News. https://adanews.ada.org/ada-news/2024/february/new-ada-guideline-recommends-nsaids-to-manage-dental-pain-in-adults-adolescents. Accessed 9/8/25.
- Ibuprofen (oral route). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/ibuprofen-oral-route/description/drg-20070602. Accessed 9/8/25.