What is a Tension Headache and How do I Treat it?
Headache
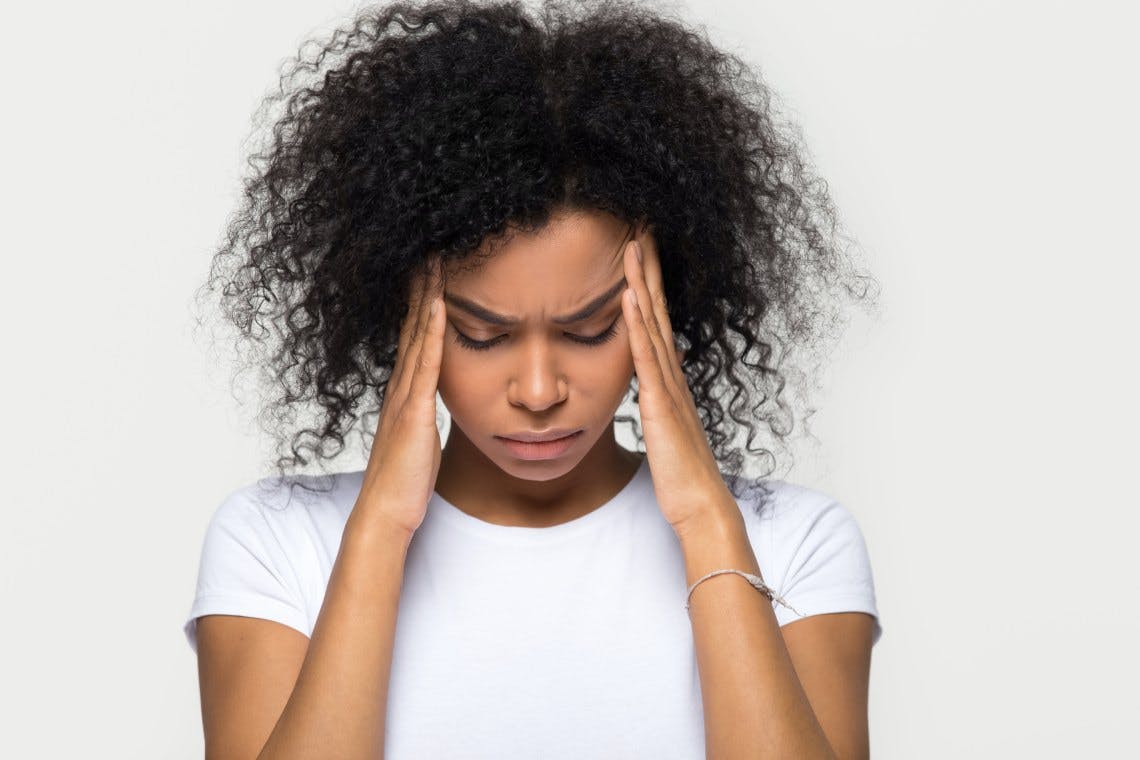

While there are many different types of headaches, tension headaches are the most common variety.1 Despite being widespread, their causes aren’t well understood. Learn what may cause a tension headache and how to find relief so you can get back to your life and the moments that matter.
What is a Tension Headache?
A tension headache is defined as a mild to moderate pain that is described as feeling like a tight band around the head.2 The pain may be localized to the head, scalp, and neck and is frequently associated with muscle tightness in these areas.1 Episodic tension headaches can last from a half hour to a week, and may become chronic.2 Chronic tension headaches last hours and may be continuous; if they occur for 15 or more days in a month over a span of three months, they’re considered chronic.2
What is the Difference Between a Tension Headache and a Migraine?
It can be difficult to distinguish what type of headache you’re having in real time. However, unlike certain types of migraines, tension headaches aren’t usually associated with nausea or visual disturbances like auras.2 Physical activity may aggravate a migraine but typically doesn’t exacerbate the pain caused by a tension headache.2
What Causes Tension Headaches?
As the name suggests, a tension headache can occur when the muscles in the neck, face, and scalp contract and become tense.1 Some research suggests that these headaches are not always linked to muscle contractions and are instead a symptom of a sensitized pain system.2 Anyone at any age may experience them, but they occur most commonly in adults and older teens.1 They run in families and may affect women more often than men.1
The most commonly reported trigger for a tension headache is stress, but depression and anxiety may also play a role.1,2 Other triggers include alcohol use, dental problems like teeth grinding, eye strain, and fatigue.1 You may also get tension headaches while you’re having a migraine.1
Some of the symptoms of a tension headache include:1,2
- Dull pressure
- Feeling as though there is a tight band around the head
- Pain all over the head, rather than at a localized point or on one side
- Pain that is worse in the scalp, temples or back of the neck
- Tenderness in the shoulder muscles as well as the head
Tension Headache Relief and Prevention
Many who experience tension headaches actively try to treat them at home. Simple pain relievers available without a prescription, like Advil Tablets, are typically a first line of treatment for reducing the pain caused by a headache.3 Combination medications may be more effective than single-ingredient pain relievers when it comes to tension headaches.3 These typically combine a pain relieving drug with caffeine in a single dose and are usually available over the counter.
Lifestyle changes may help to prevent and relieve tension headaches. Some of these remedies for headache relief and prevention include:3,4
- Managing your stress. Plan ahead and organize your day to give yourself more time to relax. If you find yourself in a situation that is overly tense or stressful, take a step back and remove yourself, if you’re able. Listen to your body, get enough sleep, drink plenty of water, and try not to skip meals.
- Applying heat or ice. A heating pad or an ice pack can help to soothe sore muscles in your neck and shoulders and can help to alleviate built-up tension.
- Adjust your posture. Good posture can keep your muscles from becoming unnecessarily tense. Stand with your shoulders back and your head level. When looking at your phone or computer, try to position the screen so that it’s level with your eyes rather than tilting your head to look at the screen.
- Try biofeedback. Work with a therapist to recognize when your muscles are becoming tense, and learn how to relax them before they cause you to develop a tension headache. Biofeedback sessions typically involves electrodes attached to your skin to detect signals from your neck and shoulder muscles. These sessions can help you recognize and manage factors that contribute to your tension headaches.
A tension headache can put your life on pause, but knowing how to manage your symptoms will have you feeling like yourself again.
Source Citations:
- Tension Headache. Medline Plus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000797.htm. Accessed on 12/7/2021.
- Tension Headache Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tension-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20353977. Accessed 12/7/2021.
- Tension Headache Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tension-headache/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353982. Accessed 12/7/2021.
- Ways to Tame Tension Headaches. Harvard School of Medicine. https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/4-ways-to-tame-tension-headaches. Accessed 12/7/2021.
By clicking the link(s) above, you will be taken to an external website that is independently operated and not managed by Haleon. Haleon assumes no responsibility for the content on the website. If you do not wish to leave this website, do not click on the links above.